Evaporation
Evaporation is a type of vaporization that occurs on the surface of a liquid as it changes into the gas phase. The surrounding gas must not be saturated with the evaporating substance. When the molecules of the liquid collide, they transfer energy to each other based on how they collide with each other.

Process of evaporation ;
Evaporation happens when a liquid substance becomes a gas. When water is heated, it evaporates. The molecules move and vibrate so quickly that they escape into the atmosphere as molecules of water vapor. ... Heat from the sun, or solar energy, powers the evaporation process.
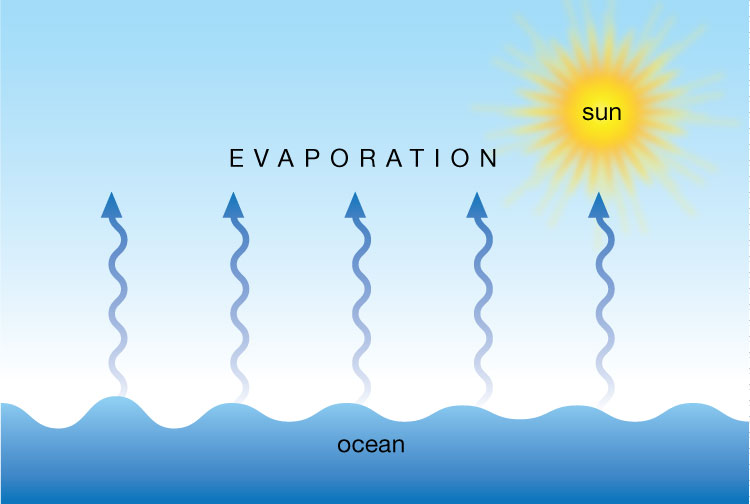
What can evaporate ?
Some examples of liquids that can evaporate at room temperature are alcohol, gasoline and water. Evaporation is the process when molecules from liquid pass to the atmosphere as gas without reaching the boiling point.
What is evaporation rate ?
An evaporation rate is the rate at which a material will vaporize (evaporate, change from liquid to vapor) compared to the rate of vaporization of a specific known material. This quantity is a ratio, therefore it is unitless.
the vaporization (evaporation) rate equals the product of the gas's mass transfer coefficient, the estuary's surface area, and the contaminant concentration in water. Thus, for our contaminant, the evaporation rate = (0.24 m per day)(day 24 h−1)(2 × 106 m2)(0.81 CW) = 16,200 CW g h−1


No comments:
Post a Comment