Lithosphere
A lithosphere is the rigid, outermost shell of a terrestrial-type planet, or natural satellite, that is defined by its rigid mechanical properties. On Earth, it is composed of the crust and the portion of the upper mantle that behaves elastically on time scales of thousands of years or greater.

The lithosphere is the solid, outer part of the earth. The lithosphere includes the brittle upper portion of the mantle and the crust, the outermost layers of Earth’s structure. It is bounded by the atmosphere above and the asthenosphere (another part of the upper mantle) below.
Although the rocks of the lithosphere are still considered elastic, they are not viscous. The asthenosphere is viscous, and the lithosphere-asthenosphere boundary (LAB) is the point where geologists and rheologists—scientists who study the flow of matter—mark the difference in ductility between the two layers of the upper mantle. Ductility measures a solid material’s ability to deform or stretch under stress. The lithosphere is far less ductile than the asthenosphere.
There are two types of lithosphere: oceanic lithosphere and continental lithosphere. Oceanic lithosphere is associated with oceanic crust, and is slightly denser than continental lithosphere.
Plate Tectonics
The most well-known feature associated with Earth’s lithosphere is tectonic activity. Tectonic activity describes the interaction of the huge slabs of lithosphere called tectonic plates.
The lithosphere is divided into tectonic plates including the North American, Caribbean, South American, Scotia, Antarctic, Eurasian, Arabian, African, Indian, Philippine, Australian, Pacific, Juan de Fuca, Cocos, and Nazca.
Most tectonic activity takes place at the boundaries of these plates, where they may collide, tear apart, or slide against each other. The movement of tectonic plates is made possible by thermal energy (heat) from the mantle part of the lithosphere. Thermal energy makes the rocks of the lithosphere more elastic.
Tectonic activity is responsible for some of Earth's most dramatic geologic events: earthquakes, volcanoes, orogeny (mountain-building), and deep ocean trenches can all be formed by tectonic activity in the lithosphere.
Tectonic activity can shape the lithosphere itself: Both oceanic and continental lithospheres are thinnest at rift valleys and ocean ridges, where tectonic plates are shifting apart from one another.
How the Lithosphere Interacts with Other Spheres
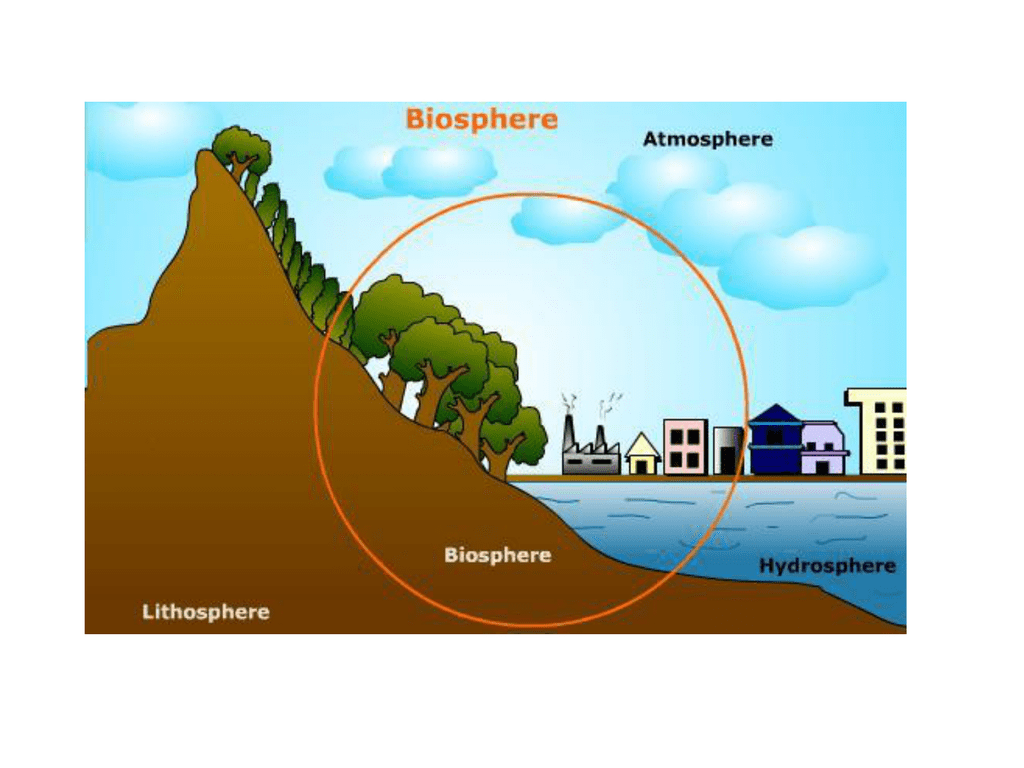
The cool, brittle lithosphere is just one of five great “spheres” that shape the environment of Earth. The other spheres are the biosphere (Earth’s living things); the cryosphere (Earth’s frozen regions, including both ice and frozen soil); the hydrosphere (Earth’s liquid water); and the atmosphere (the air surrounding our planet). These spheres interact to influence such diverse elements as ocean salinity, biodiversity, and landscape.
For instance, the pedosphere is part of the lithosphere made of soil and dirt. The pedosphere is created by the interaction of the lithosphere, atmosphere, cryosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere. Enormous, hard rocks of the lithosphere may be ground down to powder by the powerful movement of a glacier (cyrosphere). Weathering and erosion caused by wind (atmosphere) or rain (hydrosphere) may also wear down rocks in the lithosphere. The organic components of the biosphere, including plant and animal remains, mix with these eroded rocks to create fertile soil—the pedosphere.
The lithosphere also interacts with the atmosphere, hydrosphere, and cryosphere to influence temperature differences on Earth. Tall mountains, for example, often have dramatically lower temperatures than valleys or hills. The mountain range of the lithosphere is interacting with the lower air pressure of the atmosphere and the snowy precipitation of the hydrosphere to create a cool or even icy climate zone. A region’s climate zone, in turn, influences adaptations necessary for organisms of the region’s biosphere.
Extra terrestial lithosphere :
All terrestrial planets have lithospheres. The lithospheres of Mercury, Venus, and Mars are much thicker and more rigid than Earth's.